Top tourist spots in Kyrgyzstan include the large, picturesque Issyk-Kul Lake, the high-altitude Song-Kul Lake with its yurt...
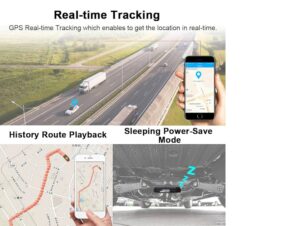
GPS assists in road navigation by providing turn-by-turn directions, real-time traffic updates, and re-routing to avoid hazards or...
Office work culture significantly impacts society by shaping economic stability, influencing public health outcomes, fostering community engagement, and...
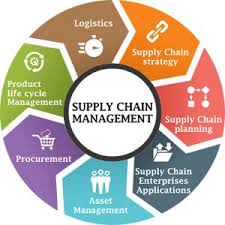
Production planning is a crucial element of supply chain and logistics, acting as the bridge between demand and...
Democracy, fundamentally, means “rule by the people.” It’s a system of government where power is held by the...